Three Important Things
1. Volatility of Few-Shot Learning
The capability of LLMs to perform few-shot learning essentially gives us a new model by just changing our prompts, bypassing the need to do any fine-tuning.
However, few-shot learning suffers from stability issues, where for instance the order in which the examples are supplied can influence the prediction of the labels significantly.
This paper aims to address this by introducing a method for calibrating the model for few-shot learning.
2. Sources of High Variance
The paper identified 3 main sources of high variance in few-shot learning.
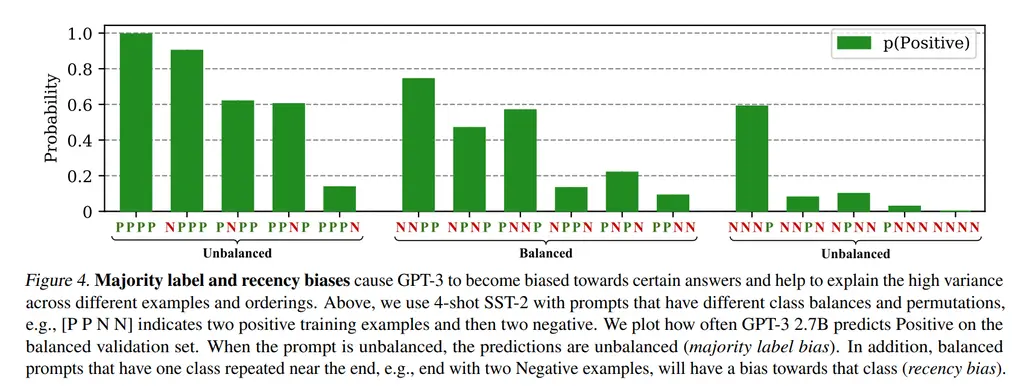
The figure above uses an example of a sentence with either positive or negative labels.
- Majority Label Bias: GPT-3 has a higher probability of outputting tokens that are the majority label. With respect to the figure above, this can be seen from both the “Unbalanced” groups, where \(p(\text{Positive})\) is either close to 1 or 0.
- Recency Bias: It also tends to output labels with a higher probability if it is more common towards the end of the few-shot examples. For instance, this can be observed in the “Balanced” regime.
- Common Token Bias: Tokens that appear in the pre-training dataset also have a higher tendency of being output. This was observed for the LAMA fact retrieval dataset, where it tends to predict common tokens like “America” instead of rarer ground-truth tokens.
3. Contextual Calibration
The authors performed calibration by first taking the output values for what is known as the content-free input. The content-free input is an example that is neutral, such as “N/A”, blank, or random gibberish. For instance, the last line in the following example is content-free:
Input: Subpar acting. Sentiment: Negative
Input: Beautiful film. Sentiment: Positive
Input: N/A Sentiment:
With the probabilities from the content-free input \(\hat{\bp}_{\text{cf}}\), they then defined a matrix to normalize it to the identity vector:
\[\bW = \text{diag}(\hat{\bp}_{\text{cf}})^{-1},\]and added the transformation \(\bW \hat{\bp}\) to the end of the output probabilities. This performs calibration by making the content-free example assign equal probability to all tokens.
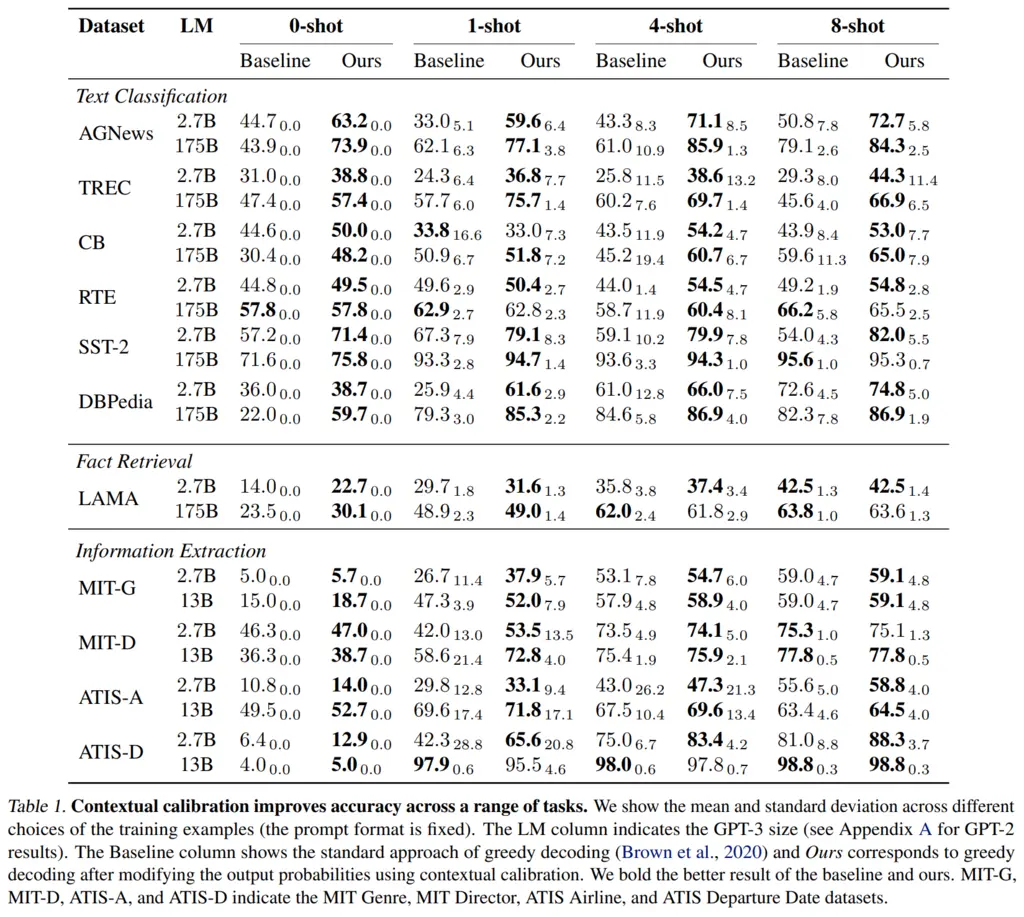
They showed that this scheme resulted in generally better performance and less variance:
Most Glaring Deficiency
Instead of using a transformation that maps the content-free example to uniform, I thought it would have made more sense to only make it uniform among the tokens that it should expect to be ever output (i.e only positive and negative for SST).
Conclusions for Future Work
Calibration is a relatively easy and non-intrusive way of improving the performance of few-shot learning; however there still remains a lot of future work to understand how exactly LLMs learn from few-shot examples and how this results in biases in its output.